Effective Pesticides to Eradicate Aphids: Strategies for Successful Gardening


Intro
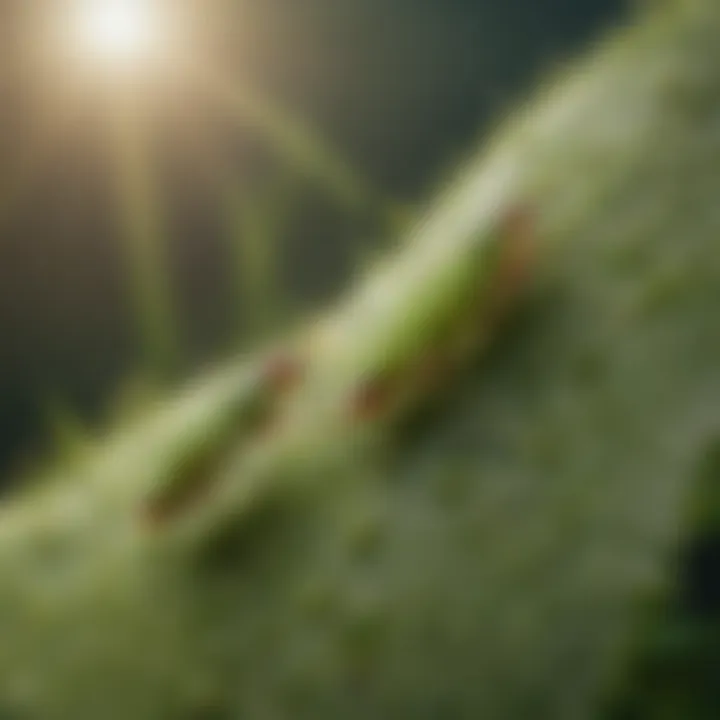
Aphids are a common pest in gardens, affecting a wide range of plants. These small insects can cause significant damage, leading to wilting, yellowing leaves, and even the death of plants. Understanding how to control them is essential for anyone passionate about gardening or horticulture. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of effective pesticides, evaluating options from chemicals to natural solutions. Each method will be assessed for its efficacy, safety, and application techniques, ensuring that gardeners can make informed decisions.
In this exploration, we will not only look into specific pesticide options but also consider integrated pest management strategies. This approach promotes sustainable practices, balancing plant health with environmental considerations. By the end of this article, the reader will be equipped with knowledge to effectively select and apply the right solutions for controlling aphids while preserving their garden's ecosystem.
Gardening Know-How
Plant Care Guides
Caring for plants means being vigilant about potential pest invasions. Recognizing early signs of aphid presence can save your plants from severe damage. Look for:
- Curling leaves
- Sticky residue on plants (honeydew)
- Black sooty mold on leaves
Seasonal Gardening Tips
Aphids tend to thrive in warmer weather. Implement preventive measures as part of your seasonal gardening routine. Here are some ideas:
- Regularly monitor your plants during spring and summer when aphids are most active.
- Encourage beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on aphids.
- Use floating row covers early in the season to protect tender plants.
DIY Garden Projects
Creating barriers is an effective way to protect plants from aphids. Some DIY options include:
- Constructing insect netting frames to shield susceptible plants.
- Planting companion plants like marigolds, which repel aphids and attract beneficial insects.
- Mixing homemade insecticidal soap with water to spray directly on affected plants.
Integrated pest management combines various control methods, creating a balanced approach for effective aphid management.
Effective Pesticides
Chemical Pesticides
Chemical pesticides offer fast-acting solutions against aphids. Some notable options include:
- Imidacloprid: A popular systemic insecticide, it is absorbed by plants and targets aphids directly.
- Pyrethroids: These synthetic chemicals provide quick knockdown effects on pest populations. Common brands include Cyhalothrin and Lambda-cyhalothrin.
While they are effective, caution is necessary. Overuse or misuse of chemical pesticides can lead to pest resistance or harm beneficial insects.
Natural Pesticides
For those inclined to organic options, several natural pesticides effectively combat aphids:
- Neem oil: Derived from the seeds of the neem tree, it disrupts aphid development and feeding.
- Insecticidal soap: Made from natural fats and oils, it suffocates aphids without harming plants.
Natural pesticides often require more frequent applications but are safer for the environment.
Homemade Solutions
For gardeners looking for cost-effective solutions, homemade remedies can be effective. Some well-known mixes include:
- Soap and water spray: Mix one tablespoon of liquid soap with one quart of water and spray directly on aphids.
- Garlic spray: Blend garlic cloves with water, strain, and spray on affected plants. This not only deters aphids but also enhances overall plant health.
Epilogue
Managing aphids isn’t just about selecting the right pesticide; it's about understanding the balance within the garden ecosystem. Integrated pest management strategies work best, considering both chemical and natural solutions. By remaining vigilant and informed, gardeners can protect their plants while promoting healthy growing conditions. Ultimately, effective pest management will lead to a more vibrant and flourishing garden.
Preamble to Aphids
Aphids are small, sap-sucking insects that can cause significant damage to gardens and crops. Their presence often goes unnoticed until substantial damage has been done. Understanding aphids is crucial to effective pest management since they target a variety of plants, weakening them and potentially leading to death. This introduction sets the stage for discussing effective pesticides and management strategies that can help gardeners combat these pests.
Understanding Aphid Biology
Aphids belong to the family Aphididae and are known for their rapid reproduction rates. Under favorable conditions, an aphid can reproduce asexually, leading to exponential population growth. They are typically found on the undersides of leaves, where they feed on phloem sap. Their piercing mouthparts facilitate this feeding, which can weaken plants, cause leaf curling, and create an environment conducive to the development of sooty mold. These insects can be green, black, or even pink, making identification challenging. Understanding their biology allows gardeners to better choose control measures that target their lifecycle effectively.
The Impact of Aphids on Plant Health
The impact of aphids on plant health cannot be overstated. They not only sap essential nutrients but also act as vectors for various plant viruses. This virus transmission can severely compromise the health of plants, leading to stunted growth and yield reduction. Affected plants might exhibit signs such as yellowing leaves, distorted growth, and reduced flowering. Furthermore, aphids excrete a substance known as honeydew, which attracts other pests and encourages fungal infections.
Key Considerations: Effective pest management requires comprehensive knowledge of aphid behavior and their effects on the garden.
In summary, recognizing the threat posed by aphids and understanding their biology and impact on plant health are pivotal for developing successful pest control strategies. The following sections will delve into pesticide options, both chemical and natural, to help gardeners manage aphid populations efficiently.
Pesticides Overview

Understanding the role of pesticides in gardening is crucial for effective aphid management. Pesticides are substances designed to prevent, control, or eliminate pests that threaten plants. This section delves into what pesticides are, their various types, and why they are essential tools for gardeners struggling with aphids.
Pesticides offer multiple benefits. They can quickly reduce aphid populations, thus protecting the health of plants. Using pesticides correctly can save time and resources during gardening. However, it is vital to consider not only the effectiveness but also the safety and environmental impact of the pesticides used.
What Are Pesticides?
Pesticides are chemicals or biological agents used to kill pests. The term encompasses a range of products, including insecticides, herbicides, fungicides, and more. In the context of aphid management, insecticides specifically target these pests.
The primary purpose of pesticides is to mitigate the damage caused by harmful organisms. Proper application can lead to healthier plants and improved yields for gardeners. Yet, mismanagement or overuse can lead to pest resistance or negative impacts on beneficial insects, which play a significant role in maintaining an ecosystem.
Types of Pesticides
There are various types of pesticides, each with specific targets and action methods. Here are the main categories:
- Chemical Pesticides: Synthetic compounds created in laboratories. Common examples include systemic insecticides like imidacloprid and contact insecticides like pyrethroids. They work effectively but may have side effects on other insects.
- Natural Pesticides: Made from naturally occurring substances. Products like neem oil and insecticidal soap fall into this category. They can be less harmful to beneficial insects and the environment.
- Biological Control Agents: This approach involves using natural predators, such as ladybugs and lacewings, to manage aphid populations. It promotes a balanced ecosystem.
- Homemade Solutions: Simple mixtures that gardeners can create at home, such as soap sprays or garlic mixtures. These remedies can be effective against aphids without using harsh chemicals.
Chemical Pesticides for Aphid Control
Chemical pesticides play a crucial role in managing aphid infestations, particularly for those who face severe outbreaks that threaten both ornamental and edible plants. These synthetic compounds are designed to quickly reduce aphid populations either by destroying the insects or by disrupting their vital physiological functions. Given the significant negative impact aphids have on plant health, as they can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and decreased yields, understanding effective chemical controls becomes essential for gardeners and horticulturists alike.
The decision to use chemical pesticides should not be taken lightly. It demands a comprehensive understanding of the specific pesticide's action, the environmental conditions, and the potential impact on non-target species, including beneficial insects such as pollinators. Recognizing these factors ensures that chemical pest control is effective while minimizing potential harm to the broader ecosystem. Moreover, the appropriate selection and application of chemical pesticides contribute significantly to overall gardening success.
Systemic Insecticides
Systemic insecticides are absorbed by plants and distributed throughout their tissues. When aphids feed on infested plants, they ingest these chemicals, resulting in their eventual mortality. This method offers certain advantages:
- Long-lasting Effect: Systemic insecticides remain effective for an extended period, providing continuous protection against new aphid arrivals.
- Targeted Action: Since the pesticide is inside the plant, it targets pests feeding directly on it, thus reducing harm to beneficial insects located externally.
However, gardeners should be mindful that systemic insecticides can have prolonged effects on the environment. The persistence of these chemicals can lead to unintended consequences, including harmful impacts on non-target flora and fauna. In addition, the choice of a specific systemic insecticide should be based on the targeted aphid species and the plants being treated.
Contact Insecticides
Contact insecticides operate differently from systemic options. These chemicals must directly touch aphids to be effective, leading to immediate results. As a result, contact insecticides are especially useful for rapid responses required during significant infestations. Key considerations include:
- Quick Knockdown: These pesticides often have a fast action, killing aphids on contact, which can provide immediate relief to affected plants.
- Application Precision: Optimal results depend on accurately applying the insecticide so that it coats the affected areas of plants.
On the downside, contact insecticides often necessitate repeated applications. Since they do not provide residual protection, it is essential to monitor and treat regularly to maintain control of aphid populations. Additionally, such pesticides may unintentionally harm beneficial insects if not used cautiously.
Selective vs. Non-Selective Pesticides
Understanding the distinction between selective and non-selective pesticides is vital for effective aphid management.
- Selective Pesticides: These products target specific pests, minimizing impact on beneficial organisms. They often have active ingredients that are less harmful to beneficial insects, making them preferable for integrated pest management strategies.
- Non-Selective Pesticides: By contrast, non-selective products affect a wider range of insects, targeting any pest that comes in contact with the chemical. This includes both harmful and beneficial species. While effective, non-selective pesticides pose greater risks to the ecosystem and should be used with caution.
Gardeners and horticulturists must carefully evaluate the type of pesticide to use based on their specific needs, ensuring that their choice aligns with their broader gardening objectives and sustainability practices.
Natural Pesticides as Alternatives
The use of natural pesticides is becoming increasingly relevant in gardening. Homeowners and professional gardeners look for effective ways to manage aphids while minimizing harm to the environment and other beneficial organisms. Natural alternatives often provide a safer approach, enabling the gardener to protect the ecosystem within their garden.
One of the key benefits of natural pesticides is their lower toxicity compared to synthetic chemicals. They are generally safer for pets, humans, and beneficial insects such as bees and ladybugs. Additionally, many natural formulations come from readily available ingredients, making them easy to implement for any gardener.
However, it is crucial to understand the effectiveness and limitations of natural pesticides. While they can control aphids effectively, results may vary. Therefore, combining approaches is often beneficial for superior results, creating a well-rounded pest management strategy that addresses various aspects of the gardening ecosystem.
Essential Oils and Natural Extracts
Essential oils and natural extracts serve as powerful tools in the treatment of aphids. They often carry strong fragrances and potent compounds that repel or kill pests. For example, oils like neem, peppermint, and rosemary possess insecticidal properties. They disrupt aphid feeding and mating, leading to reduced populations over time.
To use essential oils, blend a few drops with water and a mild soap. Spray this mixture on affected plants, focusing on the undersides of leaves where aphids tend to colonize. Regular applications help maintain control, especially during the initial stages of an aphid infestation.
When using natural extracts, it’s vital to ensure you source high-quality oils. Dilution is key—applying oils too concentrated can harm the plants themselves. Always monitor the plants' response to the treatment for any adverse reactions, adjusting the concentration as necessary.
"Natural treatments may not yield immediate results but are beneficial for long-term garden health."
Beneficial Insects and Biological Controls
Beneficial insects offer an alternative strategy for managing aphids. Ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps actively hunt aphids, significantly reducing their numbers without relying on chemical treatments. Creating an environment that attracts these beneficial insects is crucial for sustainable gardening.
To encourage beneficial insects, plant a diverse range of flowers and herbs. For example, marigolds, dill, and fennel can attract ladybugs and other predatory insects into your garden. Additionally, avoiding broad-spectrum insecticides helps preserve these pest control agents.
Monitoring aphid populations is essential when employing biological controls. Keeping track of their presence allows gardeners to introduce or protect beneficial insects at the right time. This strategy promotes a healthy garden ecosystem, balancing pest and predator relationships without relying solely on pesticides.
In summary, natural pesticides provide an effective way to manage aphids while maintaining environmental integrity. Exploring essential oils and beneficial insects can result in a sustainable and healthy garden.
Homemade Solutions for Aphid Control
Homemade solutions for aphid control provide an effective, economical, and environmentally-friendly approach to manage these pests in gardens. These DIY methods not only help mitigate aphid infestations but also allow gardeners to avoid the potentially harmful effects of synthetic pesticides. By utilizing simple ingredients from the kitchen or garden, you can create your own pest deterrents that have been proven effective through numerous anecdotes and practical experiences.
One of the key benefits of homemade solutions is their accessibility. Gardeners often have the necessary ingredients at hand, minimizing costs and eliminating the need for specialized products. Furthermore, these natural methods have a lower environmental impact, as they do not introduce synthetic chemicals into the ecosystem. This consideration is especially important for those seeking sustainable gardening practices.
Nevertheless, caution should be taken when using homemade solutions. It is essential to test any new spray on a small area of the plant first to ensure no adverse reactions occur. Proper application techniques are crucial in achieving optimal results while preserving the health of the plants.
DIY Soap Sprays
DIY soap sprays are a widely recognized solution for controlling aphids. They work by suffocating the pests when the spray coats their bodies. The effectiveness of this method lies in the choice of soap. Use a mild liquid soap, such as castile soap or dish soap without additives. Avoid detergents containing degreasers or fragrances, as they may harm beneficial insects or the plants themselves.
To create a homemade soap spray, mix about two tablespoons of soap with one quart of water in a spray bottle. Shake well to ensure the soap dissolves completely. Focus on spraying the undersides of leaves and the stems, as aphids tend to inhabit these areas. Applying the soap spray every few days can help control the aphid populations, especially during periods of high infestation.
"Homemade soap sprays offer a direct way to eliminate aphids without harming beneficial insects when used carefully."
Garlic and Hot Pepper Mixtures
Garlic and hot pepper mixtures serve as another potent homemade solution to deter aphids. Garlic contains chemicals that repel pests while hot peppers contain capsaicin, known for its irritation effect on insects. Combining these ingredients can create a powerful spray that both repels and may kill aphids.
To prepare this mixture, blend a few cloves of garlic with a specified amount of water. Strain the mixture to remove solid particles, then add crushed hot pepper or hot pepper flakes. Finally, add a few drops of mild soap to help the mixture adhere to plant surfaces.
After diluting this potent mixture with water, spray it onto the affected plants, especially focusing on areas with visible aphid activity. Reapply every week or after rainfall for continued effectiveness.
Utilizing homemade solutions, like soap sprays and garlic mixtures, cultivates a proactive approach to aphid control while navigating the delicate balance of the garden ecosystem. This DIY method empowers gardeners and contributes to healthier plant growth.
Application Techniques for Effective Pest Control
Effective pest control hinges not only on the choice of pesticide but also on its application. Without proper techniques, even the best products can fail, leading to continued aphid infestation. Understanding application methods enhances the efficacy of the chosen solutions, ensuring that they reach the target pests while minimizing waste or environmental harm.
Effective application techniques help to maximize the impact of pesticides. This can be measured in terms of speed, coverage, and penetration into the plant tissues where aphids reside. Proper techniques also reduce the overall quantities of pesticides needed, which has obvious benefits for the environment and personal health. Additionally, these methods contribute to the development of a sustainable pest management strategy, which is vital in contemporary gardening practices.
Timing and Frequency of Application
The timing of pesticide application is critical in managing aphid populations effectively. It is essential to assess the life cycle of aphids to determine the most effective moments to intervene. Early treatment, particularly when aphids are in their initial stages of infestation, vastly increases the chances of complete eradication.
Furthermore, the frequency of applications depends on the type of pesticide used. For chemical pesticides, adhering to the recommended intervals is crucial. This ensures that residues remain effective against newly hatched aphids. In contrast, natural solutions typically require more frequent application due to their shorter effective lifespan.
Key considerations include:
- Weather Conditions: Apply pesticides during dry periods to enhance adherence and reduce wash-off by rain.
- Growth Stage of Plants: Younger plants might be more sensitive to chemical treatments, thus requiring careful management.
- Life Cycle Monitoring: Regularly check for new aphid populations to adjust application timing accordingly.
Spraying Techniques for Coverage
When applying pesticides, the technique used to spray can greatly impact the overall effectiveness of the treatment. An even and thorough coverage is essential to ensure that all areas of the plant, including the undersides of leaves where aphids often congregate, are treated.
Consider adopting the following spraying techniques:
- Use of Proper Equipment: A high-quality spray nozzle can help in achieving better coverage. Consider using a backpack sprayer or a hose-end sprayer for larger areas.
- Flat and Uniform Spray Pattern: Aim for a consistent spray pattern to avoid patches that could allow aphid populations to persist.
- Angle and Distance: Adjust the angle of spraying to facilitate thorough coverage. Typically a 45-degree angle works best for achieving coverage in dense foliage.
- Multiple Passes: If necessary, make multiple passes to ensure all areas are treated. This is particularly important for densely packed plants.
Proper application not only safeguards your plants but also promotes the responsible use of chemicals, aligning with sustainable gardening practices.
Implementing these techniques demonstrates a commitment to effective pest control while promoting environmental stewardship. With a systematic approach to timing and application methods, gardeners can significantly mitigate the threat posed by aphids.
Safety Considerations in Pesticide Use
The use of pesticides in gardens, while effective for pest control, carries significant safety considerations that cannot be overlooked. Homeowners and gardening enthusiasts must prioritize safety to protect themselves, their families, and the environment. Understanding proper use, handling, and storage of pesticides helps minimize risks associated with their application.
Proper Handling and Storage
Handling pesticides safely is crucial in preventing accidental exposure. The following key points should be considered:
- Read Labels Carefully: Before using any pesticide, always read the label thoroughly. It contains essential information regarding dosage, application methods, and safety precautions.
- Use Protective Gear: When applying pesticides, wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves, masks, and goggles. This reduces the risk of skin contact and inhalation.
- Store Pesticides Safely: Keep pesticides in their original containers and store them in a cool, dry place away from children and pets. Lockable storage cabinets are ideal to prevent unauthorized access.
Improper storage can lead to leaks or spills, which could pose risks to human health and the environment. Regularly check for expired products and dispose of them according to local regulations.
Environmental Impact of Pesticides
Pesticides can have broad environmental implications. It is important to be aware of these impacts to foster a sustainable approach to gardening:
- Soil Health: Some chemical pesticides can disrupt soil microbial communities, harming beneficial organisms that contribute to soil fertility.
- Water Contamination: If not applied correctly, pesticides may run off into nearby waterways, contaminating drinking water sources and harming aquatic life.
- Biodiversity Loss: Overuse of non-selective pesticides can lead to a decline in beneficial insects, such as pollinators, which are crucial for healthy ecosystems.
- Biological Accumulation: Pesticides can accumulate in the food chain, potentially leading to toxicity in plants and animals.
It is essential to weigh the benefits of pest control against these environmental risks.
Adoption of integrated pest management practices can help minimize these impacts, ensuring safer use of chemicals while improving overall garden health. By considering these safety aspects in pesticide use, gardeners can effectively manage aphids while being conscientious stewards of their environment.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies


Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an essential approach to managing aphid populations effectively. This strategy incorporates multiple techniques to minimize reliance on chemical pesticides while promoting the health of the garden ecosystem. IPM recognizes that diverse strategies can lead to significant pest control with reduced risks to beneficial organisms, human health, and the environment.
One prominent aspect of IPM is its holistic nature. By combining biological, mechanical, and cultural practices alongside targeted pesticide use, gardeners can create a more balanced approach to pest management. This multifaceted view facilitates not just the short-term resolution of aphid infestations, but also addresses the underlying issues that contribute to pest problems, improving the garden's resilience in the long term.
Advantages of adopting IPM include:
- Reduced pesticide use, which leads to lower chemical exposure for people and pets.
- Conservation of beneficial insects that assist in the ecosystem, such as ladybugs and lacewings.
- Cost-effectiveness by carefully selecting treatments based on monitoring results.
- Increased plant health due to a broader focus on overall gardening practices.
While implementing IPM strategies, it is important to consider factors such as the types of plants affected, the environment, and seasonal variations. Each garden is unique, and thus strategies must be tailored to specific situations for maximum effectiveness.
"The best pest control is the prevention of pest problems in the first place."
Combining Methods for Effective Control
To effectively combat aphids, combining several methods enhances the success of the control measures. This can involve the integration of chemical, natural, and physical control strategies. By leveraging each method's strengths, gardeners can achieve better outcomes than when relying solely on one approach.
For instance, using a natural pesticide like neem oil can decrease aphid populations. However, monitoring the plant health with attention to beneficial insects can amplify results. Regular inspections help identify the presence of beneficial species and notably inform when to apply chemical treatments if necessary.
Some methods to consider for effective control are:
- Cultural methods: Rotate plants, use resistant varieties, and optimize plant spacing to improve air circulation around crops.
- Mechanical methods: Handpicking aphids or utilizing insect vacuums can provide immediate relief if the infestation is small.
- Biological control: Encourage beneficial predators, such as ladybugs, to establish a population in the garden.
Monitoring and Assessing Aphid Populations
Monitoring aphid populations is a crucial element of IPM. Effective monitoring helps gardeners respond promptly to infestations, reducing damage to plants and improving the timing of interventions. Gardeners can employ various strategies for monitoring, such as anecdotal observations or structured methods like using yellow sticky traps to capture aphids and assess their numbers more accurately.
Assessing the population dynamics includes:
- Regular plant inspections, focusing on the undersides of leaves where aphids tend to congregate.
- Keeping records of aphid populations over time to recognize patterns and anticipate future outbreaks.
- Evaluating the presence of natural enemies in the garden and assessing their effectiveness in reducing aphid numbers.
By maintaining a proactive approach to monitoring, gardeners can make informed decisions about when and how to implement specific control strategies. This approach proves beneficial, preventing minor issues from evolving into major infestation crises.
Case Studies: Successful Aphid Management
Aphids present a significant challenge for gardeners and horticulturists. However, examining real-life case studies sheds light on effective strategies employed in various scenarios. This section emphasizes the value of learning from these experiences. Case studies illustrate how different approaches impact pest control success. They also reveal valuable insights into how integrating various methods can enhance results.
Residential Gardening Success Stories
Many homeowners successfully manage aphid infestations through innovative approaches. One exemplary case involves a suburban garden where organic methods were predominantly used. The gardener observed aphid populations rising during the spring months, impacting flowering plants. To tackle this challenge, the gardener employed a mixture of natural pesticides and beneficial insects.
Key steps from this success story:
- Attracting Beneficial Insects: The gardener planted flowers like marigolds to attract ladybugs and lacewings. These insects are natural predators of aphids and helped keep the population in check.
- Natural Sprays: The gardener created a homemade soap spray using liquid dish soap and water. This solution smothered aphids upon contact, reducing their numbers without harming beneficial insects.
- Monitoring and Adaptation: Regular observations allowed the gardener to adjust the strategy when needed. By understanding the life cycle of aphids, timely actions were taken to prevent overwhelming infestations.
The positive outcomes from this garden not only displayed effective aphid management but also encouraged sustainable practices.
Commercial Horticulture Practices
In a commercial setting, aphid management requires a systematic approach. A nursery that specializes in ornamental plants adopted integrated pest management techniques for successful aphid control. The business faced significant aphid pressure due to the sheer volume of plants and the susceptibility of some species.
Effective strategies utilized in this case include:
- Implementing IPM Principles: The nursery applied the principles of integrated pest management. This included regular scouting for early signs of aphid activity, which allowed faster response times.
- Utilizing Biological Control Agents: The nursery collaborated with suppliers to introduce parasitic wasps, which specifically target and control aphid populations effectively.
- Careful Selection of Chemical Pesticides: When chemical intervention was necessary, the nursery opted for selective systemic insecticides. They chose products like Imidacloprid, targeting aphids while minimizing impact on beneficial insects.
By focusing on environmentally conscious practices, the nursery maintained healthy plant growth and achieved better market performance.
"Learning from both residential and commercial practices provides gardeners at all levels with insights into effective aphid management strategies."
These case studies not only highlight the successful management of aphids but also emphasize the need for adaptability and observation in any gardening context.
Ending and Future Directions
The final aspect of managing aphids and maintaining garden health centers on assessing the efficacy of current practices. This is an essential theme throughout the article, revealing how effective pest control strategies directly impact plant health and productivity. Ongoing evaluation of the methods used helps gardeners adapt and improve these practices over time. Moreover, this reflection allows for a comparison of results across various approaches, be they chemical, natural, or homemade.
Assessing Efficacy of Current Practices
Evaluating pesticide effectiveness involves looking at several important factors. One key consideration is the level of aphid infestation before and after treatment. Monitoring should also include how quickly the aphid population responds and whether any beneficial insects are affected. Furthermore, understanding the persistence of the pesticide's effects informs future application decisions.
- How long does a treatment remain effective?
- Are certain methods leading to a resurgence of the aphids?
- Are there any unintended consequences for non-target species in the garden?
In-depth studies can increase awareness about the long-term impact of chemical versus natural solutions. By paying attention to variable factors, homeowners can refine their pest management strategies, improving outcomes for their gardens.
The Path Toward Sustainable Gardening
Looking ahead, sustainable gardening practices must become the focal point in combating aphid infestations. This entails integrating various strategies that not only manage pests effectively but also promote overall ecosystem health. Homeowners can explore the use of integrated pest management, which blends biological, cultural, and mechanical controls with chemical options.
The benefits of sustainable gardening are far-reaching:
- Environmental health: Reducing reliance on harsh chemicals preserves biodiversity.
- Personal health: Homegrown produce free from harmful substances is safer to consume.
- Economic sustainability: Long-term use of sustainable methods can lower costs associated with continuous pesticide purchases.
As gardeners shift toward these approaches, they must prioritize plant resilience and ecosystem balance. Ongoing education and adaptation will be vital in this journey, fostering a more sustainable gardening practice while striving to create a thriving garden environment for years to come.







